Fermi–Pasta–Ulam problem
In physics, the Fermi–Pasta–Ulam problem or FPU problem was the apparent paradox in chaos theory that many complicated enough physical systems exhibited almost exactly periodic behavior instead of ergodic behavior. One of the resolutions of the paradox includes the insight that many non-linear equations are exactly integrable. Another may be that ergodic behavior may depend on the initial energy of the system.
Contents |
The FPU experiment
In the Summer of 1953 Fermi, Pasta, Ulam and Mary Tsingou conducted numerical experiments (i.e. computer simulations) of a vibrating string that included a non-linear term (quadratic in one test, cubic in another, and a piecewise linear approximation to a cubic in a third). They found that the behavior of the system was quite different from what intuition would have led them to expect. Fermi thought that after many iterations, the system would exhibit thermalization, an ergodic behavior in which the influence of the initial modes of vibration fade and the system becomes more or less random with all modes excited more or less equally. Instead, the system exhibited a very complicated quasi-periodic behavior. They published their results in a Los Alamos technical report in 1955. (Note: Enrico Fermi died in 1954 and so this technical report was published after Fermi's death.)
The FPU experiment was important both in showing the complexity of nonlinear system behavior and the value of computer simulation in analyzing systems.
The FPU lattice system
Fermi, Pasta and Ulam (FPU) simulated the vibrating string by solving the following discrete system of nearest-neighbor coupled oscillators. We follow the explanation as given in Palais's article. Let there be N oscillators representing a string of length l with equilibrium positions 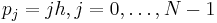 where
where 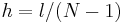 is the lattice spacing. Then the position of the jth oscillator as a function of is
is the lattice spacing. Then the position of the jth oscillator as a function of is 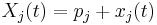 so that
so that 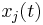 gives the displacement from equilibrium. FPU used the following equations of motion:
gives the displacement from equilibrium. FPU used the following equations of motion:
(Note: this equation is not equivalent to the classical one given in the French version of the article)
This is just Newton's second law for the jth particle. The first factor 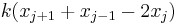 is just the usual Hooke's law form for the force. The factor with
is just the usual Hooke's law form for the force. The factor with 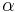 is the nonlinear force. We can rewrite this in terms of continuum quantities by defining
is the nonlinear force. We can rewrite this in terms of continuum quantities by defining 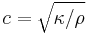 to be the wave speed, where
to be the wave speed, where 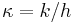 is the Young's modulus for the string and
is the Young's modulus for the string and 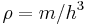 is the density:
is the density:
Connection to the KdV equation
The continuum limit of the governing equations for the string (with the quadratic force term) is the Korteweg–de Vries equation (KdV equation.) The discovery of this relationship and of the soliton solutions of the KdV equation by Kruskal and Zabusky in 1965 was an important step forward in nonlinear system research. We reproduce below a derivation of this limit, which is rather tricky, as found in Palais's article. Beginning from the "continuum form" of the lattice equations above, we first define u(x,t) to be the displacement of the string at position x and time t. We'll then want a correspondence so that 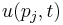 is
is 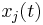 .
.
We can use Taylor's theorem to rewrite the second factor for small 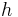 , (subscripts of u denote partial derivatives):
, (subscripts of u denote partial derivatives):
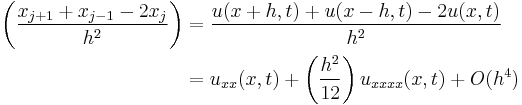 .
.
Similarly, the second term in the third factor is:
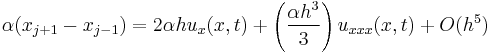 .
.
Thus, the FPU system is:
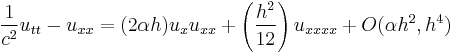 .
.
If one were to keep terms up to O(h) only and assume that 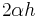 approaches a limit, the resulting equation is one which develops shocks, which is not observed. Thus one keeps the O(h^2) term as well:
approaches a limit, the resulting equation is one which develops shocks, which is not observed. Thus one keeps the O(h^2) term as well:
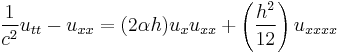 .
.
We now make the following substitutions, motivated by the decomposition of traveling wave solutions (of the ordinary wave equation, to which this reduces when 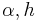 vanish) into left- and right-moving waves, so that we only consider a right-moving wave. Let
vanish) into left- and right-moving waves, so that we only consider a right-moving wave. Let 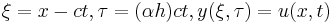 . Under this change of coordinates, the equation becomes:
. Under this change of coordinates, the equation becomes:
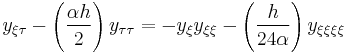 .
.
To take the continuum limit, assume that 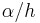 tends to a constant and
tends to a constant and 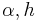 tend to zero. If we take
tend to zero. If we take 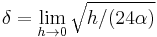 , then:
, then:
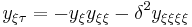 .
.
Taking 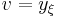 results in the KdV equation:
results in the KdV equation:
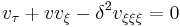 .
.
Zabusky and Kruskal argued that it was the fact that soliton solutions of the KdV equation can pass through one another without affecting the asymptotic shapes that explained the quasi-periodicity of the waves in the FPU experiment. In short, thermalization could not occur because of a certain "soliton symmetry" in the system which broke ergodicity.
References
- E. Fermi, J. Pasta, and S. Ulam, Studies of Nonlinear Problems, Document LA-1940 (May 1955)
- N.J. Zabusky and M.D. Kruskal. Interactions of solitons in a collisionless plasma and the recurrence of initial states, PRL 15 (1965), 240-243.
- R. Palais, The Symmetries of Solitons, Bulletin of the AMS 34 (1997), 339-403.
- Gallavotti, Giovanni, ed (2008) (in English). The Fermi-Pasta-Ulam Problem: A Status Report. Lecture Notes in Physics. 728. Springer. ISBN 978-3-540-72994-5. http://www.springer.com/physics/theoretical%2C+mathematical+%26+computational+physics/book/978-3-540-72994-5.
- M.A. Porter, N.J. Zabusky, B. Hu, and D.K. Campbell, "Fermi, Pasta, Ulam and the Birth of Experimental Mathematics", American Scientist 97, 6 (2009), 214-221.
External links
- Fermi-Pasta-Ulam nonlinear lattice oscillations at Scholarpedia, curated by Thierry Dauxois and Stefano Ruffo.
![m\ddot{x}_j=k(x_{j%2B1}%2Bx_{j-1}-2x_j)[1%2B\alpha(x_{j%2B1}-x_{j-1})]](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/57068894b43dfa0d7ccd83b9bf91c749.png)
![\ddot{x}_j=\frac{c^2}{h^2}(x_{j%2B1}%2Bx_{j-1}-2x_j)[1%2B\alpha(x_{j%2B1}-x_{j-1})]](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/bc0e23b4e83abb171886651280ff5407.png)
![\ddot{x}_j=c^2\left(\frac{x_{j%2B1}%2Bx_{j-1}-2x_j}{h^2}\right)[1%2B\alpha(x_{j%2B1}-x_{j-1})]](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/c357c94a0b4bb175228db08f91576a1b.png)